Abstract
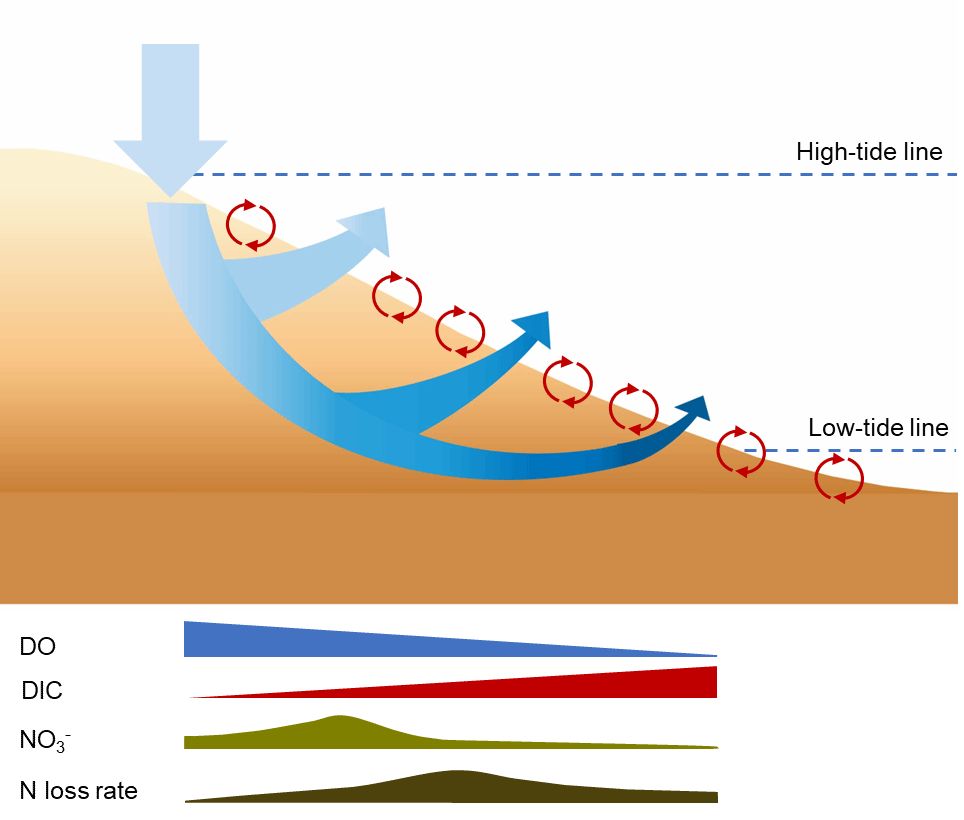
Sandy beaches are an important passage for the transport of various forms of nitrogen from land to sea. However, export fluxes of these forms of nitrogen and the mechanisms controlling their transformation remain elusive. Using the 224Ra/228Th disequilibrium approach, we estimated export fluxes of dissolved inorganic carbon and dissolved inorganic nitrogen at three intertidal sandy beaches with distinct slopes along the southeast China's coast. We identified that sandy beaches are a hotspot of nitrogen loss in the coastal ecosystem, with nitrogen removal rates reaching up to 87.1 mmolN m−2 d−1 and removal efficiencies varying between 7% and 82%. Notably, nitrogen removal rates peaked at intermediate seawater percolation fluxes, reflecting the optimal balance of oxygen consumption, marine organic matter remineralization, and nitrate production for fueling denitrification in the beach's interior. In addition, total nitrogen removal increased with beach slopes. This is likely due to the fact that steeper beaches facilitate seawater to percolate more efficiently into the beach's interior and travel along a longer flow path before it drains out, thus allowing denitrification to prevail. Overall, our field observations reveal that instead of the surface “skin circulation,” the “body circulation” system within an intertidal beach governs fluid transport and solute exchange between land and sea. We conclude that intertidal sandy beaches function as an efficient biogeochemical reactor, which attenuates anthropogenic nitrogen inputs to the coastal ocean.
Wei, L., Cai, P., Hong, Q., Wu, T., Liu, W., Cheng, Y., and Mi, P. (2026). Rapid nitrogen removal in sandy beaches driven by periodic tidal inundations. Limnology and Oceanography, 71(1), 107–123.
https://doi.org/10.1002/lno.70314