Abstract
Aquaculture sector growth is challenged by feed constraints, particularly the erratic availability and cost of fishmeal and oil from wild forage fish. Limited attention is given to the risks that forage fish shortfalls pose to aquaculture feed supplies. Here we develop a shortfall impact model to investigate the effects of varying forage fish supply scenarios on global fed aquaculture. Results suggest fisheries management interventions and persistent climate impact could reduce forage fish catches by 4.5% to 19.4%, resulting in an 8% to 35.2% decline in fed aquaculture production. Countries cultivating carnivorous species and leading aquaculture-producing nations are most affected. To sustain production, 1.8 million tonnes of alternative ingredients annually will be required, highlighting the urgent need for cost-effective alternatives to ensure resilience.
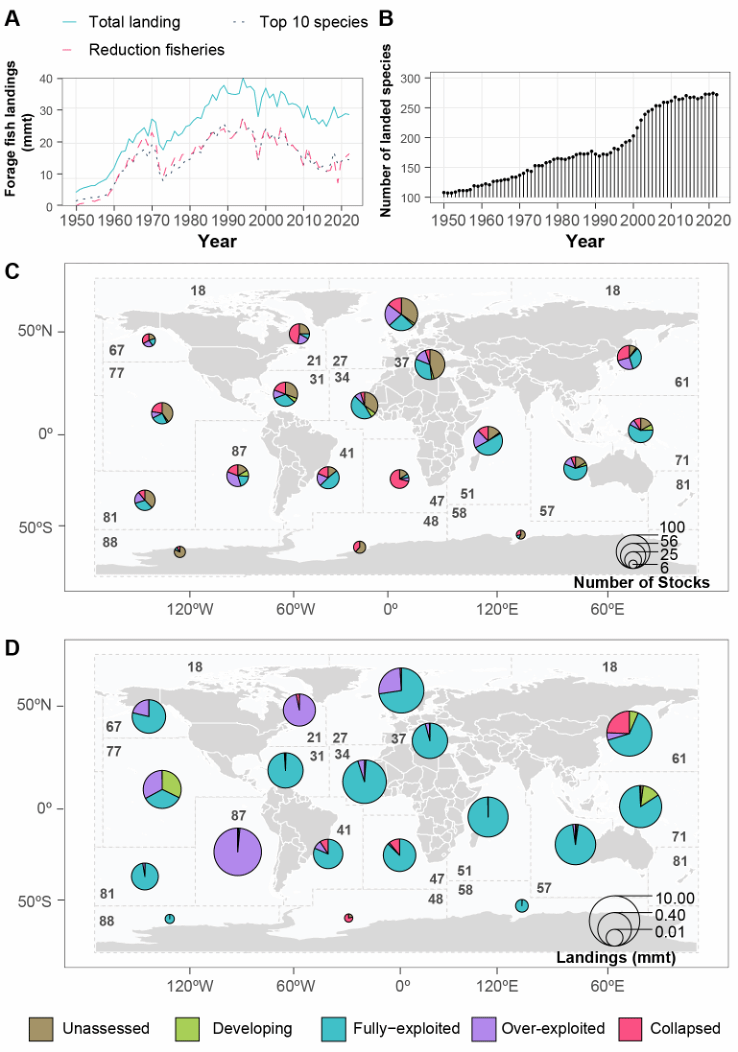
Liu, Y., Jiang, Z., Cottrell, R.S. et al. Unstable supply and future shortages of wild forage fish heighten risks to global fed aquaculture production. Nature Food (2025).
https://doi.org/10.1038/s43016-025-01254-4