Abstract
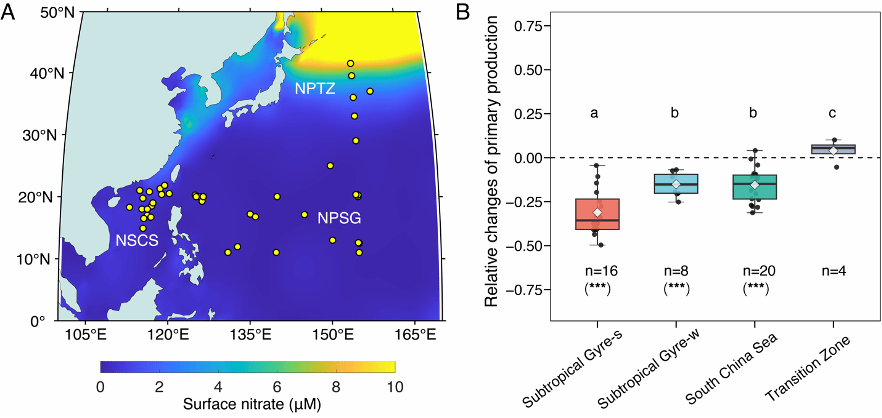
Ocean acidification caused by increasing anthropogenic CO2 is expected to impact marine phytoplankton productivity, yet the extent and even direction of these changes are not well constrained. Here, we investigate the responses of phytoplankton community composition and productivity to acidification across the western North Pacific. Consistent reductions in primary production were observed under acidified conditions in the North Pacific Subtropical Gyre and the northern South China Sea, whereas no significant changes were found at the northern boundary of the subtropical gyre. While prokaryotic phytoplankton showed little or positive responses to high CO2, small (<20 µm) eukaryotic phytoplankton which are primarily limited by low ambient nitrogen drove the observed decrease in community primary production. Extrapolating these results to global tropical and subtropical oceans predicts a potential decrease of about 5 Pg C y−1 in primary production in low Chl-a oligotrophic regions, which are anticipated to experience both acidification and stratification in the future.
Dai R.#, Wen Z.#, Hong H.#, Browning T.J., Hu X., Chen Z., Liu X., Dai M., Morel F.M.M.*, Shi D.* 2025. Eukaryotic phytoplankton drive a decrease in primary production in response to elevated CO2 in the tropical and subtropical ocean. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 122: e2423680122
https://www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/pnas.2423680122